头骨三维重建方法及其在生物考古学中的应用
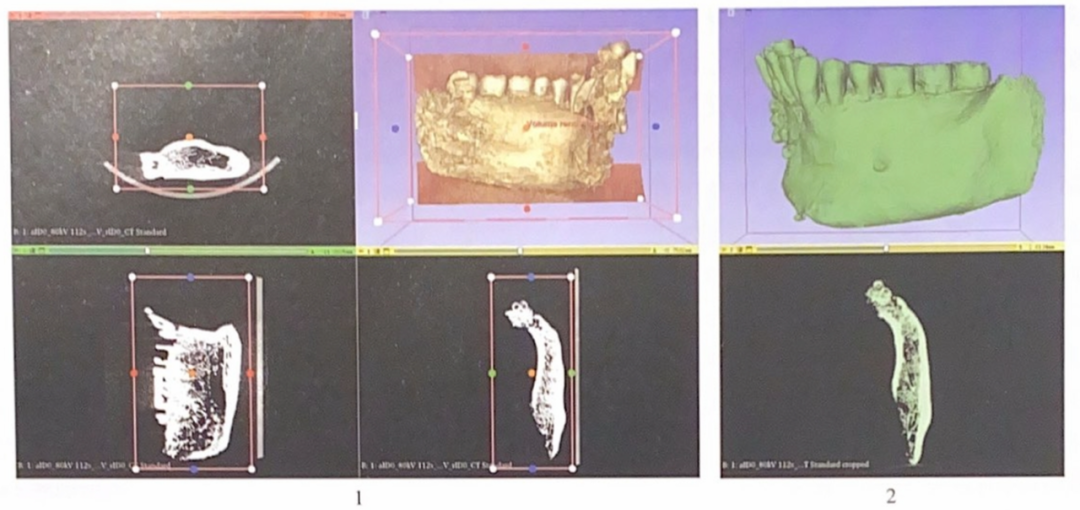
我们较多使用了美国NextEngine非接触式彩色激光扫描仪(型号为2020i)。扫描设置及扫描结果的编辑均在该扫描仪的配套软件“扫描工作室”(Scan Studio)完成。扫描时,根据骨骼形态特征及实际需求设置扫描方式、纹理捕捉模式、目标颜色、扫描精度等参数。一般情况下,理想的骨骼模型应满足如下四个基本条件,即整体较为完整清晰,细节能较好地呈现,模型文件大小适中,扫描时间较短。由于单次扫描无法获取骨骼完整的三维数据,需要从多角度获取扫描对象的三维数据。通过测试,我们发现扫描两次即可获得较为完整的形态数据(图二,1、2)。扫描完成后,可对两次扫描所获取的三维数据进行拼接并导出(图二,3)。


1.分层环绕拍摄 2.使用Context Capture三维建模 3.使用MeshLab合并模型





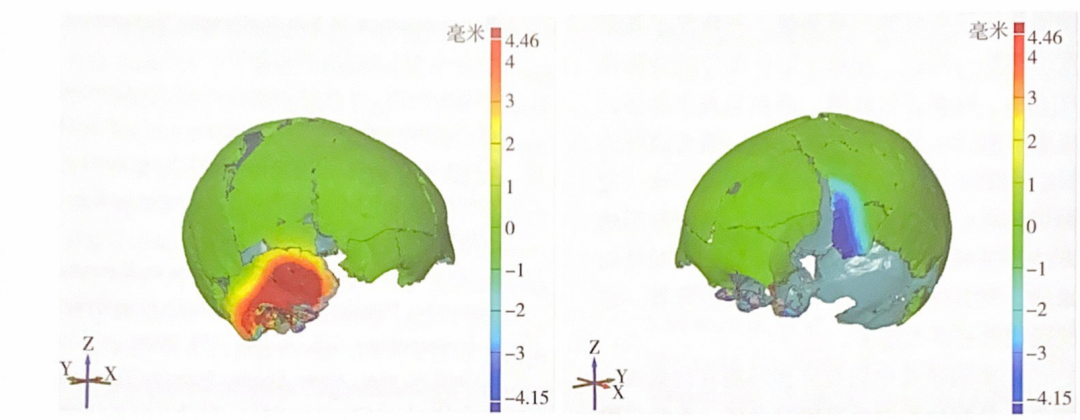
图九 顶蛳山遗址M35颅骨形变矫正的GOM Inspect拟合分析
[1]李法军:《生物人类学》(第二版)第9、10页,中山大学出版社,2020年。
[2] a.Lyman R.L,Vertebrate Taphonomy,Cambridge:Cambridge University Press,1994.
b.Ponce de León M.S.,Zollikofer C.P,New Evidence from Le Moustier 1:Computer-Assisted Reconstruction and Morphometry of the Skull,The Anatomical Record, 254(4),pp.474-489,1999.
[3]a.朱泓:《中国南方地区的古代种族》,《吉林大学社会科学学报》2002年第3期。
b.李法军等:《鲤鱼墩——一个华南新石器时代遗址的生物考古学研究》第20页,中山大学出版社,2013年。
[4]同[2]b
[5] a.Ponce de León M.S,Computerized Paleoanthropology and Neanderthals: The Case of Le Moustier 1,Evolutionary Anthropology,11,pp.68-72.2003.
b.Zollikofer C.P.E.,et al..Virtual Cranial Reconstruction of Sahelanthropus Tchadensis,Nature,434,pp.755-759,2005.
c.Ogihara N.,et al,Computerized Restoration of Nonhomogeneous Deformation of a Fossil Cranium Based on Bilateral Symmetry. American Journal of Physical Anthropology.130(1).pp.1-9.2006.
[6] a.Vialet A.L'évolution de L'homme en Eurasie:Nouveaux Fossiles,Nouveaux Outils D'analyse,L'Anthropologie, 113,pp.245-254,2009.
b.Vialet A,et al,Homo Erectus from the Yunxian and Nankin Chinese Sites: Anthropological Insights Using 3D Virtual Imaging Techniques,Comptes Rendus Palevol,9(6-7),pp.331-339,2010.
[7] a.Gunz P.,et al.,Principles for the Virtual Reconstruction of Hominin Crania, Journal of Human Evolution,57(1).pp.48-62,2009.
b.Schlager S.,et al.Retrodeformation of Fossil Specimens Based on 3D Bilateral Semi-Landmarks:Implementation in the R package"Morpho",PLoS ONE,13(3), e0194073,2018.
[8] a.吴秀杰等:《福建漳平奇和洞发现的新石器时代早期人类头骨》,《人类学学报》2014年第4期。
b.崔娅铭:《现代各主要人群中面部3D几何形态的对比》,《人类学学报》2016年第1期;《现代各主要人群额骨3D几何形态的对比》,《人类学学报》2018年第2期。
c.张亚盟:《枕骨三维形态在现生人群间的变异》,《人类学学报》2020年第4期。
[9] a.Zhang Q.,et al, Intentional Cranial Modification from the Houtaomuga Site in Jilin,China:Earliest Evidence and Longest in Situ Practice During the Neolithic Age,American Journal of Physical Anthropology,169(4),pp747-756,2019.
b.Zhang Y.M.,et al.An Early Holocene Human Skull From Zhaoguo Cave, Southwestern China,American Journal of Physical Anthropology,175(3).pp.599-610,2021.
[10]金涛等:《逆向工程技术研究进展》,《中国机械工程》2002年第16期。
[11]Weber G.W.Virtual Anthropology,Yearbook of Physical Anthropology, 156, pp.22-42,2015.
[12]Ronald V.P.J.,et al.,Dimensional Accuracy and Repeatability of the Next Engine Laser Scanner For Use in Osteology and Forensic Anthropology.Journal of Archaeological Science:Report,25,pp.308-319,2019.
[13] a.Luhmann T.,et al.,Close Range Photogrammetry: Principles, Techniques and Applications,Scotland:Whittles Publishing,pp.2-3,2006.
b.Evin A.,et al.,The Use of Close-Range Photogrammetry in Zooarchaeology: Creating Accurate 3D Models of Wolf Crania to Study Dog Domestication, Journal of Archaeological Science:Reports,9,pp.87-93,2016.
[14]Scaggion G.,et al.,3D Digital Dental Models' Accuracy for Anthropological Study Comparing Close-Range Photogrammetry to μ-CT Scanning. Digital Applications in Archaeology and Cultural Heritage,27,e00245,2022
[15] a.Grawood R.,Dunlop J.,The Walking Dead:Blender as a Tool for Paleontologists with a Case Study on Extinct Arachnids,Journal of Paleontology,88(4).pp.735-746,2014.
b.Ganry L.,et al.,Use of the 3D Surgical Modeling Technique with Open-source Software for Mandibular Fibula Free Flap Reconstruction and its Surgical Guides, Journal of Stomatology Oral & Maxillfacial Surgery,118,pp.197-202,2017
c.Woodley K., et al.,The Virtual Goniometer: Demonstrating a New Method for Measuring Angles on Archaeological Materials Using Fragmentary Bone, Archaeological and Anthropological Sciences,13,p.106,2021.
[16]a.同[6]b。
b.He L.T.,et al.,Diachronic Changes in Craniofacial Morphology among the Middle-Late Holocene Populations from Hehuang Region, Northwest China,American Journal of Physical Anthropology,169(1),pp.55-65,2019.
c.Wu X.J.,et al.,Morphological Description and Evolutionary Significance of 300 ka Hominin Facial Bones from Hualongdong,China,Journal of Human Evolution,161,103052,2021.
[17]a.Benazzi S,et al,Comparing 3D Virtual Methods for Hemimandibular Body Reconstruction,The Anatomical Record,294(7),pp.1116-1125,2011.
b.Menazii S.,et al,Geometric Morphometric Methods for Bone Reconstruction: The Mandibular Condylar Process of Picodella Mirandola,The Anatomical Record, 292(8),pp.1088-1097,2009.
c.Neeser R.,et al.,Comparing the Accuracy and Precision of Three Techniques Used for Estimating Missing Landmarks When Reconstructing Fossil Hominin Crania,American Journal of Physical Anthropology,140(1),pp.1-18,2009
d.Benazzi S.,et al.,A New OH5 Reconstruction with an Assessment of its Uncertainty,Journal of Human Evolution,61(1),pp.78-88,2011.
[18] a.同[6]a。
b.同[6]b。
c.DeVries R.P, et al.,Reproducible Digital Restoration of Fossils Using Blender,Frontiers in Earth Science,10,833379,2022
[19]Sederberg T.W.,Parry S.R.,Free-Form Deformation of Solid Geometric Models,ACM SIGGRAPH Computer Graphics,20(4),pp.151-160,1986.
[20]a.王婧超等:《自由网格变形技术在涡轮叶片多学科设计优化过程中的应用》,《飞机设计》2006年第3期。
b.汤传吉等:《基于FFD的点云变形技术研究》,《新型工业化》2012年第2期。
[21] a.同[6]a.
b.同[6]b。
